Advances in Neurology: Understanding the Nervous System
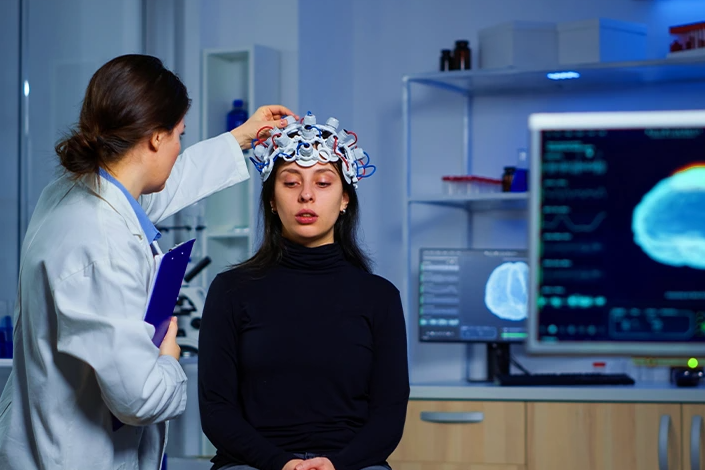
Introduction to Neurology
Neurology is a specialized branch of medicine focusing on disorders of the nervous system. This includes the brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and muscles. Neurologists diagnose and treat a wide range of neurological conditions that can affect movement, sensation, cognition, and overall bodily functions.
The Scope of Neurology
The nervous system is incredibly complex, and neurology many areas within it. These include diseases such as epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, stroke, and migraines. The field also involves understanding the mechanisms behind neurodegenerative disorders and developing new treatments.
Common Neurological Disorders
Stroke and Its Impact
Stroke occurs when blood flow to a part of the brain is interrupted, leading to tissue damage. It is a leading cause of disability worldwide. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to improve recovery chances and reduce long-term effects.
Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Issues
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive disorder that affects movement control. Symptoms include tremors, stiffness, and slowed movements. Neurologists often manage this condition with medication and sometimes surgical interventions.
Epilepsy and Seizure Management
Epilepsy involves recurrent seizures caused by abnormal electrical activity in the brain. Treatment typically includes anti-seizure medications, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgery or neurostimulation therapies.
Diagnostic Tools in Neurology
Modern neurology relies on various diagnostic techniques to assess neurological health accurately.
Imaging Techniques
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) scans provide detailed images of the brain and spinal cord. These tools help identify tumors, lesions, or areas affected by stroke.
Electrophysiological Tests
Electroencephalography (EEG) records electrical activity in the brain, assisting in diagnosing epilepsy and other disorders. Nerve conduction studies evaluate peripheral nerve function.
Lumbar Puncture
Analyzing cerebrospinal fluid obtained through a lumbar puncture can reveal infections, inflammation, or bleeding in the nervous system.
See also: AI Image Generator: Transforming Creativity with Technology
Treatment Approaches in Neurology
Treatment depends on the specific disorder and its severity. It may involve medications, physical therapy, or surgical procedures.
Medication Management
Neurologists prescribe drugs to manage symptoms, control disease progression, or prevent complications. Examples include dopamine agonists for Parkinson’s and antiepileptics for seizure control.
Rehabilitation Therapies
Physical, occupational, and speech therapies support recovery and help patients regain independence after neurological injuries.
Surgical Interventions
In some cases, surgery is necessary to remove tumors, repair nerve damage, or implant devices like deep brain stimulators.
Research and Innovations in Neurology
Ongoing research aims to improve understanding and treatment of neurological diseases.
Neuroplasticity and Recovery
Studies on neuroplasticity reveal the brain’s ability to reorganize and form new connections, offering hope for better rehabilitation strategies.
Advances in Neuroimaging
Enhanced imaging techniques allow earlier detection and more precise mapping of neurological conditions.
Emerging Therapies
Gene therapy, stem cell research, and novel drug developments show promise in treating previously untreatable neurological disorders.
The Importance of Neurology in Healthcare
Neurology plays a critical role in maintaining quality of life for individuals affected by nervous system disorders. Early intervention and continuous care can significantly impact outcomes.
Conclusion
The field of neurology continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements and research breakthroughs. Understanding the complexities of the nervous system and effectively managing its disorders remain central to improving patient care and outcomes.